Generative AI is transforming industries, with 72% of companies deploying AI solutions. Oracle leverages advanced generative AI agents combining large language models, natural language processing and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to execute complex , multi-step workflows, and integrate with existing business processes.
Explore what Oracle AI agents are, how they work, their use cases, and their benefits.
What are Oracle AI agents?
OCI generative AI agents is a fully managed service that integrates large language models (LLMs) with an intelligent retrieval system. It is designed to provide contextually relevant answers by searching a specified knowledge base.
Oracle has announced the development and integration of over 50 AI agents within its Fusion Cloud Applications Suite, targeting areas such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, quality control, sales, and customer service. These AI agents are designed to handle multi-step processes, adapt to novel situations, and respond to natural language prompts, offering more flexibility and precision than previous rule-based systems.
OCI generative AI Agents offers multiple methods for onboarding data, enabling users and their customers to interact with the data through a chat interface or an API.
Key Features
- Supports various data onboarding methods and interaction channels (chat interface or API).
- Generates contextually relevant answers by retrieving information from a knowledge base.
- Provides source attribution for all answers.
- Offers hybrid search capabilities, combining lexical and semantic approaches.
- Includes content moderation for both input and output.
- Supports multi-turn conversations, allowing users to ask follow-up questions that take prior context into account.
- Can interpret data from two-axis charts and reference tables in PDFs without requiring explicit descriptions of visual elements.
- Extracts and displays hyperlinks present in PDF documents in the chat responses.
How does Oracle AI agents work?
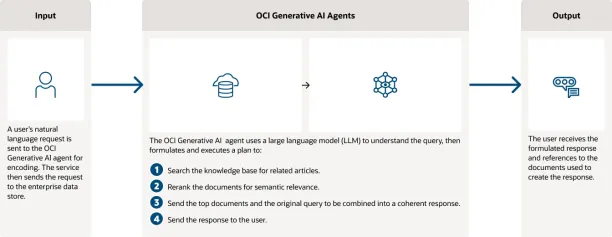
- Input: User Query
- A user submits a natural language query to the OCI Generative AI Agent.
- The service encodes the query and sends it to the enterprise data store (the knowledge base) for processing.
- Processing: Query Understanding and Plan Formulation
- The AI agent, powered by a large language model (LLM), interprets the query.
- It formulates and executes a plan to generate a response. This involves the following steps:
- Searching the knowledge base for relevant articles or documents.
- Re-ranking the retrieved documents based on semantic relevance.
- Combining the most relevant documents and the user query to generate a coherent and contextually accurate response.
- Output: Response Delivery
- The agent sends the formulated response back to the user.
- The response includes references to the documents or sources that were used to generate the answer.
Knowledge base data types
There are two different ways you can provide data for OCI Generative AI Agents to use as a knowledge base. A knowledge base is essentially the collection of information or documents that the AI agent searches to generate answers. Here’s a breakdown of what each type means:
1. Service-managed option
This option allows you to store your data in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage. With this approach, you can:
- Upload up to 1,000 files, either text or PDF documents, each with a maximum size of 100 MB.
- Request a limit increase through Oracle support to store more or larger files.
This is a simple way to manage your knowledge base using Oracle’s infrastructure without setting up additional systems.
2. Bring Your Own (BYO) Options
This option allows you to use your existing systems to host and manage the data the AI agent will access. Oracle provides integration with specific tools for this purpose. It is available on systems like:
- Oracle Database 23c (AI vector search): This is a database that supports advanced search capabilities, including vector search, which helps the AI agent retrieve relevant data more effectively.
- OCI Search with OpenSearch: This option uses OpenSearch, a search engine technology, to index and manage your data. It allows the agent to perform efficient searches on the ingested and indexed data.
This option gives you flexibility and control if you already have an infrastructure for storing and managing data. You can integrate the AI agent into your existing systems without migrating data to OCI Object Storage.
14 Oracle generative AI agents use cases
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) agents combine retrieval and language generation capabilities to produce accurate and context-aware responses. The agent retrieves relevant documents or data and generates coherent answers based on this information. Example use cases include:
- Customer service automation: A customer service AI agent can streamline customer service by handling queries through conversational interfaces, retrieving knowledge base data, and escalating complex issues to human agents. This ensures faster issue resolution and enhances user satisfaction. Automation also reduces repetitive tasks, allowing customer support teams to focus on personalized and higher-value interactions.
- Legal research: AI agents can assist legal professionals by rapidly searching vast databases for precedents and case law. These capabilities improve efficient execution of planning and research tasks. By simplifying complex searches, AI supports quicker decision-making, ensuring legal teams meet deadlines and deliver accurate advice to their clients.
- Financial analysis and reporting: AI agents assist financial teams in analyzing data, detecting anomalies, and generating comprehensive reports. They synthesize insights from diverse sources like market news and internal reports. Such tools improve financial management by streamlining processes, suggesting corrective actions, and enhancing decision-making accuracy for budgeting, forecasting, and performance evaluation.
- Educational tutoring: AI agents act as personal tutors by providing tailored learning resources and clarifying complex concepts. These systems adapt to student needs, offering interactive educational content and step-by-step guidance. By automating resource retrieval, they help learners achieve academic goals while enabling educators to focus on innovative teaching strategies.
- Content creation: AI supports content creators by retrieving relevant information, analyzing trends, and drafting suggestions for articles, reports, or presentations. These agents accelerate the creative process while maintaining originality. By leveraging advanced AI capabilities, they enable professionals to focus on refining content quality and connecting with their audience effectively.
- Technical support: AI agents guide users through troubleshooting by synthesizing technical manuals and forums into concise solutions. They resolve issues efficiently, minimizing downtime. These agents empower support teams by reducing workload and delivering consistent, accurate resolutions, significantly enhancing user experience in technical environments.
- Supply chain management: AI agents optimize supply chain operations by aggregating data on inventory, suppliers, and logistics. They analyze trends for actionable insights, enabling businesses to reduce inefficiencies and ensure smooth operations. Such tools play a crucial role in improving overall business processes and achieving operational excellence.
- Supplier onboarding: A supplier-onboarding agent could facilitate the integration of new suppliers by automatically pulling relevant documents, verifying compliance with company policies, and updating supplier records in the enterprise system.
- Real estate analysis: AI agents support real estate professionals by synthesizing property data and market trends. They provide insights on pricing, demand, and investment opportunities, aiding decision-making. With AI-driven analysis, professionals can adapt to dynamic market conditions and deliver tailored advice to clients effectively.
- Travel planning: AI agents serve as personalized travel guides by recommending destinations, local attractions, and itineraries. They create customized experiences based on user preferences, simplifying travel arrangements. By integrating diverse data sources, these agents enhance user satisfaction and empower travelers with unique, efficient planning options.
- Sales procurement assistance: A document-processing AI agent can assist a sales executive in managing procurement tasks. For example, the executive could take a photo of a price quote from an overseas vendor using their phone. The agent would:
- Extract the relevant information from the document.
- Translate the text, for instance, from Japanese into English.
- Create a purchase request based on the extracted data. Later, the same agent could automate the processing of the vendor’s invoice, flagging it for review by a payment manager.
- Sales call analysis: In sales, an AI agent could analyze customer interactions during sales calls, extracting insights such as customer preferences or key objections, and generating detailed reports for sales teams to improve future engagements.
- Talent management and hiring: AI agents can be used to identify and analyze job candidates, helping HR teams streamline talent acquisition. Hypothetically, an agent might search for suitable candidates across databases, evaluate their resumes, and provide recommendations based on predefined job requirements.
- Quality control in manufacturing: AI agents monitor production data, identify patterns indicating defects, and recommend adjustments to ensure quality standards. By leveraging advanced analytics, they enable manufacturers to minimize waste, improve efficiency, and maintain consistency. This proactive approach ensures superior product quality and customer satisfaction.
Explore general Agentic AI use cases with some real-life examples.
Oracle GenAI agents benefits
- Transparency: Enables tracking of responses back to their sources for clarity and accountability.
- Continuous Updates: Data sources can be updated without interrupting the functionality of the agent.
- Scalability and Security: Operates on a scalable and secure architecture designed for growing demands while maintaining data integrity.
- Incremental Ingestion: Allows precise data updates through incremental ingestion and version control.
- Improved Interactions: Facilitates natural and intuitive interactions, enhancing customer experience.
Latest developments: Oracle AI Agents RAG capabilities
The OCI Generative AI RAG Agent was officially released on September 25, 2024, after a beta version was previously announced. The new RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) Agents introduced several enhancements compared to the existing OCI Generative AI Agents:
- Integration with Oracle Database 23ai: Oracle Database 23ai adds advanced vector search for unstructured data like text and images. It enables more precise and relevant search outcomes by converting data into vector representations. This allows for seamless handling of complex queries and integration of structured and unstructured data.
- Streamlined set-up: Simplified setup process with an improved user interface. It allows users with limited technical expertise to deploy RAG agents quickly and easily.Fewer steps and a more intuitive experience reduce setup time and effort.
- Improved response quality and relevance: State-of-the-art LLMs provide higher-quality and more accurate responses. It ensures that conversational interactions are more insightful and contextually appropriate, making AI interactions more valuable for users across various domains.
- Advanced data retrieval and reranking: Enhanced data retrieval and reranking functions sift through vast data sets and prioritize relevant information. It improves the depth and precision of the AI’s responses, particularly for nuanced queries.
- Hybrid search: Combines traditional keyword searches with semantic search. It ensures the retrieval of more relevant results for both structured and unstructured data. It enhances the accuracy and quality of search outcomes.
- Managed knowledge bases: Integrated vector store and robust data ingestion pipeline for unstructured data. It simplifies storage, retrieval, and indexing of complex data. It offers efficient management of knowledge bases as a ready-to-use solution.
- Support for BYO knowledge bases with OpenSearch: Streamlined support for Bring Your Own (BYO) OCI Search with OpenSearch. It provides flexibility and control over custom search configurations. It simplifies integration with existing OpenSearch systems.
- Content moderation: Robust filtering to flag harmful or inappropriate content in input and output. It maintains safe and secure AI interactions.
- Multimodality: Processes and integrates data from multiple formats, including text, images, charts, and graphs. It delivers more comprehensive and context-rich responses. It expands the range of use cases, making the agent versatile for business needs.
FAQs
Which AI does Oracle use?
Oracle employs a variety of AI technologies to enhance functionality, drive innovation, and improve user experiences:
Embedded generative AI in business applications: Integrates generative AI in Oracle Cloud Applications for insights without altering interfaces.
OCI generative AI: Offers Cohere and Meta models in a managed environment with fine-tuning and API-based integration.
OCI generative AI agents: Combines large language models (LLMs) with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for accurate, enterprise-specific responses.
Oracle code assist: Provides an AI code companion for Java, SuiteScript, PL/SQL, and OCI development.
OCI data science: Supports building, training, and managing custom LLMs with tools like Hugging Face Transformers and PyTorch.
OCI AI infrastructure: Delivers high-performance compute resources with NVIDIA GPU-powered instances for LLM workloads.
AI vector search in Oracle database 23c AI: Enhances search with AI vectors for precise results.
HeatWave GenAI: Offers in-database LLMs and vector storage without requiring additional expertise or costs.
Autonomous database select AI: Uses LLMs to process natural language queries and generate Oracle SQL.
Further reading
External sources
Source link
#Top #Cases #Benefits



















 “>
“>
 “>
“>
![[2412.02056] A Multi-way Parallel Named Entity Annotated Corpus for English, Tamil and Sinhala [2412.02056] A Multi-way Parallel Named Entity Annotated Corpus for English, Tamil and Sinhala](https://i0.wp.com/arxiv.org/static/browse/0.3.4/images/arxiv-logo-fb.png?w=1200&resize=1200,700&ssl=1)









