“In easy phrases, we use genetic instruments that enable us to inject mice with a drug that artificially makes astrocytes specific another gene or protein of curiosity once they change into energetic,” says Wookbong Kwon, a biotechnologist at Baylor School and co-author of the research.
These proteins of curiosity have been primarily fluorescent proteins that make cells fluoresce brilliant purple. This fashion, the staff may spot the astrocytes in mouse brains that turned energetic throughout studying situations. As soon as the tagging system was in place, Williamson and his colleagues gave their mice a little bit scare.
“It’s referred to as concern conditioning, and it’s a very easy concept. You’re taking a mouse, put it into a brand new field, one it’s by no means seen earlier than. Whereas the mouse explores this new field, we simply apply a collection {of electrical} shocks by the ground,” Williamson explains. A mouse handled this manner remembers this as an disagreeable expertise and associates it with contextual cues just like the field’s look, the smells and sounds current, and so forth.
The tagging system lit up all astrocytes that expressed the c-Fos gene in response to concern conditioning. Williamson’s staff inferred that that is the place the reminiscence is saved within the mouse’s mind. Realizing that, they may transfer on to the following query, which was if and the way astrocytes and engram neurons interacted throughout this course of.
Modulating engram neurons
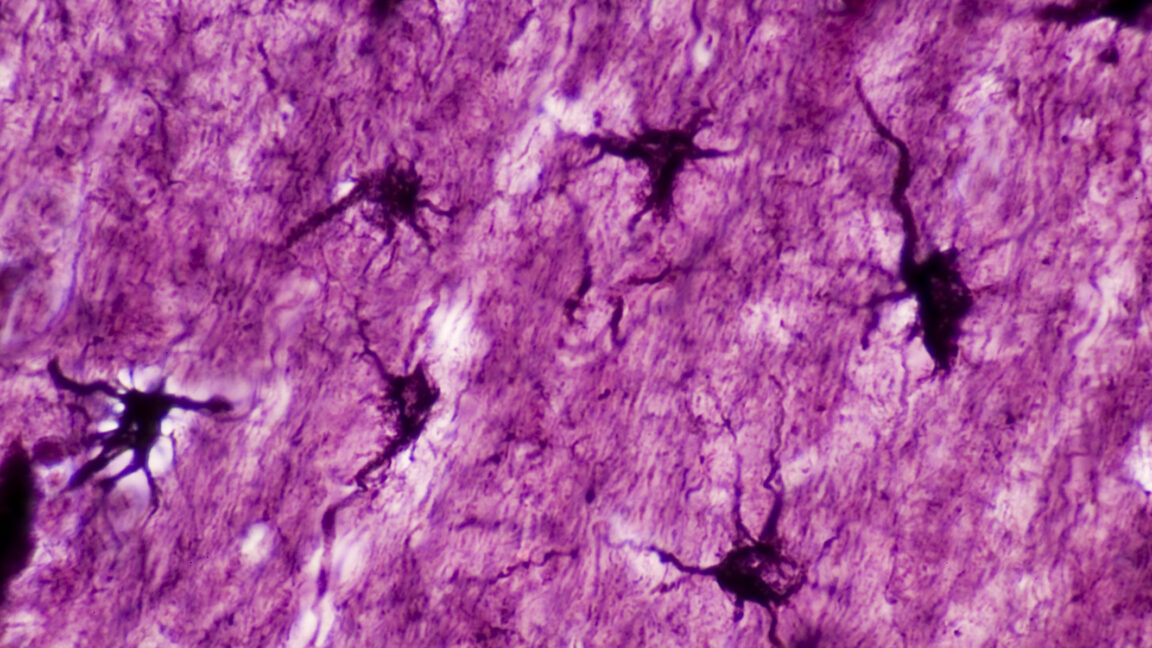
“Astrocytes are actually bushy,” Williamson says. They’ve a posh morphology with tons and many micro or nanoscale processes that infiltrate the world surrounding them. A single astrocyte can contact roughly 100,000 synapses, and never all of them will probably be concerned in studying occasions. So the staff regarded for correlations between astrocytes activated throughout reminiscence formation and the neurons that have been tagged on the identical time.
Source link
#Astrocytes #play #key #position #reminiscence






























